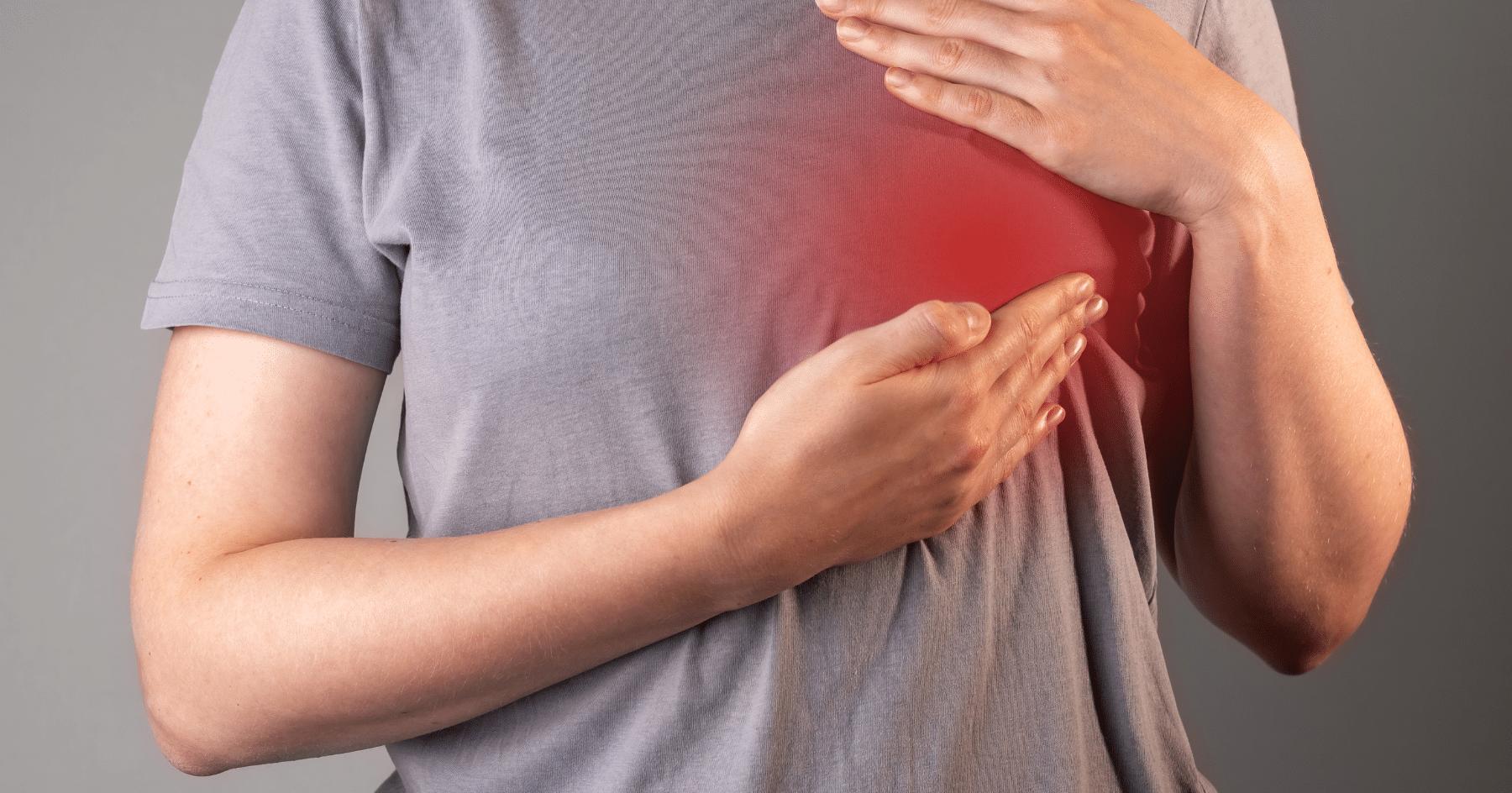
What is a Fungating Tumour
A fungating breast tumour is an advanced form of cancer that leads to the development of ulcers or infection on the skin of the breast or its vicinity. This type of tumour emerges when the cancerous mass breaks through the skin, resulting in the formation of a wound or ulcer characterized by leakage, an unpleasant odour and pain.
- Embarazo semana a semana
- Improving Insulin Sensitivity for People with Diabetes: Easy Ways to Incorporate Bone Broth into Your Everyday Diet
- Why Does My Skin Feel Sticky After a Shower? With Solutions
- Veal Scallopini with Lemon Caper Sauce
- How to resolve the git error "fatal cannot do a partial commit during a merge"
Fungating tumours are rare , and if they do develop, they are more likely to occur with skin cancer, breast cancer, or head and neck cancer, as these cancers can occur close to the skin. Approximately 2-5% of locally advanced breast cancers develop into a fungating breast wound.
Bạn đang xem: FUNGATING BREAST CANCER
Causes of Fungating Breast Cancer
Larger breast tumours can grow to a point where they break through the skin and form an ulcer. In some cases, the tumour can initially grow undetected and present with ulceration. However, most times the tumour is neglected and grows to this point.
If left untreated for months or years, this can grow upwards giving the characteristic appearance of a fungating breast tumor. Fungating tumours can occur in two different ways, including:
Primary Tumour:
Primary tumours develop from cancerous breast cells. When a primary tumour becomes ulcerative, it means the breast cancer cells have penetrated the skin and caused the lesions or ulcers to occur.
Secondary Tumour:
Secondary tumours spread from another site of cancer other than the breast. The cancer cells originate in a different organ and spread through the blood and lymphatic system into the breast. This is a rare occurrence.
What Stage of Breast Cancer is Fungating?
Xem thêm : No Roux Gumbo Recipe
In breast cancer, TNM staging is commonly used. Fungating tumours are commonly found in more advanced stages of breast cancer, including stages 3 or 4. At these stages, the cancer has often spread to nearby tissues or distant organs and is harder to treat. However, there can be some exceptions to this.
- Stage 3: The cancer is often larger and can be found in more lymph nodes and/or invasion of the chest wall or skin around the breast, but the cancer has not spread to the bones or organs.
- Stage 4: Breast cancer can now be found in other parts of the body, having spread through lymphatic channels or the bloodstream, from the breast and lymph nodes. The most common sites are bones, lungs, liver, and brain. The cancer is now considered metastatic or advanced.
What are the Symptoms of Fungating Breast Cancer?
A fungating tumour can start as a shiny, red lump on the skin. If the lump begins to break down, this can look like a sore, and the wound might get bigger if left untreated. In more serious cases the tumour can spread into the surrounding skin, or grow deeper into structures of the chest wall, such as muscle and bones, and form holes.
Fungating tumours can cause a variety of symptoms, in addition to any symptoms that the underlying cancer may cause. These can include:
Unpleasant Smell
A distinctive symptom of fungating breast cancer is the presence of an unpleasant odour coming from the open wounds or ulcers.
Visible Tumour Growth
Fungating breast tumours cause significant changes in the appearance of the breast, and patients may visibly notice the tumour growth outside of the skin’s surface.
Pain, Discomfort and Bleeding
The presence of open wounds, infiltration of surrounding tissues, and nerve damage from the advanced tumour can contribute to persistent pain. These tumours can lead to the development of open wounds that leak fluid or blood as a result of damaged skin from the tumour growth.
Xem thêm : Gold Bond : Body Lotions & Creams
This can further contribute to the overall physical and emotional burden experienced by individuals with fungating breast cancer. Therefore, treatment is often focussed on alleviating pain and bleeding to improve quality of life. Patients can experience some physical and psychosocial side effects due to the complications associated with fungating breast cancer. Receiving social and psychosocial support is an essential component of treatment.
Who Does Fungating Breast Cancer Affect?
Fungating breast cancer primarily impacts those with more advanced stages of breast cancer. Patients who have not received timely medical intervention, or who have experienced disease progression despite undergoing treatment, are at a higher risk of fungating breast cancer.
Life Expectancy with Fungating Breast Cancer
A patient’s life expectancy can vary depending on factors such as:
- the stage or type of cancer
- a patient’s overall health
- the effectiveness of available treatments
It is not always possible to prevent a fungating tumour from occurring. However, early detection and treatment of a tumour may help. In general, the larger the tumour grows, the more likely it is to penetrate the skin and cause ulceration. However, even small tumours can cause ulceration. A person should consider getting regular screenings and talking with their doctor about any unusual lumps.
Unfortunately, fungating breast cancer often occurs in larger, more advanced stages of breast cancer, which may negatively impact overall life expectancy. Your treating doctor or cancer specialist will discuss treatment options with you, and in some cases, the potential for palliative care can influence outcomes.
Treatments and Care for Fungating Wounds
Treating breast cancer often involves a multimodality approach, and managing fungating breast cancer involves addressing the symptoms and providing supportive care to enhance the individual’s quality of life. Treatment options can include:
Nguồn: https://buycookiesonline.eu
Danh mục: Info
This post was last modified on November 29, 2024 3:29 pm