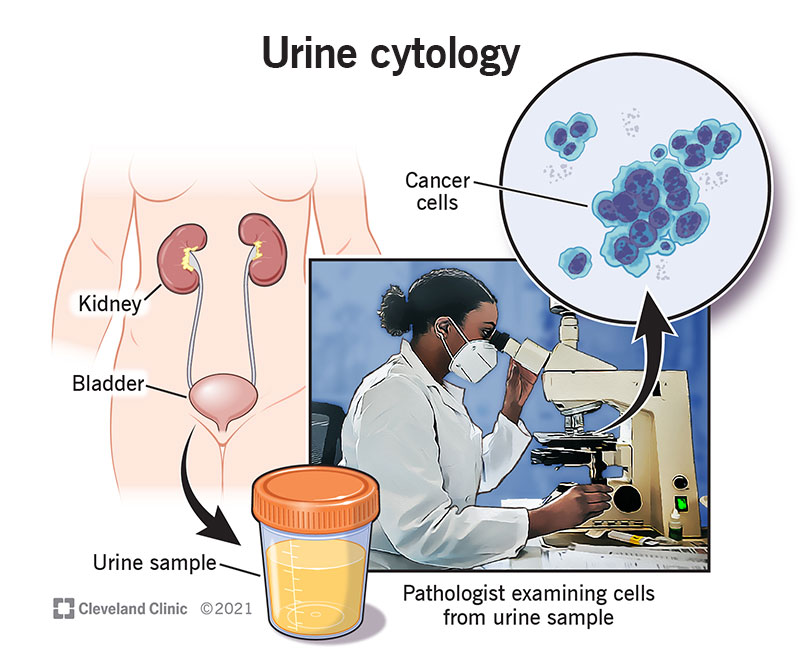
What is a urine cytology test?
A urine cytology test screens your urine for precancer or cancer cells. A physician called a cytopathologist examines the cells in your urine sample under a microscope to look for abnormalities.
What is cytology?
Cytology is the examination of single cells from bodily tissues or fluids. A specialized physician called a cytopathologist examines the cells in the tissue or fluid sample under a microscope and looks for certain characteristics or abnormalities in the cells.
Bạn đang xem: Urine Cytology
What is a urine cytology test used for?
A urine cytology test can help diagnose cancers of the urinary system, including:
- Bladder cancer.
- Cancer of the ureter (the narrow tube that carries urine from your kidney to your bladder).
- Cancer of the urethra (the narrow tube that carries your urine from your bladder out of your body.
- Kidney cancer, among others.
Healthcare providers often perform other tests and procedures alongside urine cytology tests to diagnose urinary system cancers.
Urine cytology tests can also detect cytomegalovirus, a herpes virus, and other viral diseases.
Is urine cytology the same as urinalysis?
Xem thêm : Coding for Hepatitis C
While urine cytology and urinalysis are both diagnostic tests that involve your urine (pee), they are different.
Urine cytology is a more specific test that involves looking at cells in a sample of urine under a microscope. A pathologist most commonly looks for cancer cells specifically.
A urinalysis is a urine screening test. Healthcare providers use it to discover and manage many different diseases and conditions, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney disease and diabetes.
A urinalysis involves examining the appearance, concentration and content of the urine. It can detect cells, cell fragments or certain substances, like crystals, protein or glucose (sugar), in your urine.
Though your provider may ask you to have a urinalysis for a specific reason, providers often use urinalysis as a routine or yearly screening. On the other hand, urine cytology tests are less common and are often used for very specific reasons.
When would a urine cytology test be needed?
Xem thêm : Trial of the Worm
Your healthcare provider may want to do a urine cytology test if you’re experiencing signs or symptoms of a urinary system cancer, including:
- Having blood in your pee (hematuria).
- Experiencing frequent pain when you pee.
- Experiencing a burning sensation when you pee.
Urine cytology tests can help find some types of cancers, however, there are limitations. Just because a urine cytology test doesn’t find cancer cells, it doesn’t necessarily mean that the person is cancer-free. Because of this, healthcare providers often have the person have other tests alongside urine cytology tests and may repeat urine cytology at a later date.
Other reasons your healthcare provider might have you give a urine sample for a urine cytology test include:
- To check for cancer recurrence if you’ve had bladder cancer and have been treated for it.
- To monitor bacteria in your pee if you have frequent (recurrent) urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- To test for certain viral diseases.
Who performs a urine cytology test?
In most cases, the person who is having a urine cytology test will pee into a sterile cup in a private bathroom. This is known as a clean catch urine sample. Sometimes the person or a healthcare provider needs to insert a catheter (a narrow tube that’s inserted into your urethra to reach your bladder) in order to collect a urine sample
A healthcare provider can also collect a urine sample for a cytology test during a cystoscopy, which is a procedure in which the provider uses a thin scope to examine the inside of your bladder and urethra.
The healthcare provider then sends the urine sample to a laboratory for testing. A scientist called a pathologist, or cytopathologist, examines the cells in the urine sample under a microscope and determines and prepares a report.
Nguồn: https://buycookiesonline.eu
Danh mục: Info