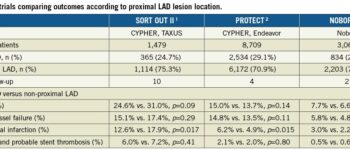
Where is the spine located?
Your spine is the long column of bones that extend from your neck to your lower back. Your spine starts at the base of your skull (head bone) and ends at your tailbone, a part of your pelvis (the large bony structure between your abdomen and legs).
What does the spine look like?
A healthy spine has three natural curves that make an S-shape. These curves work as shock absorbers to protect your spine from injury.
Bạn đang xem: Spine Structure and Function
Xem thêm : Phlebotomy
Several bones and soft tissues make up your spine. They connect like bricks, stacked one on top of the other and help support your body in different ways.
What are the parts of the spine?
- Vertebrae: Your spine has 33 stacked vertebrae (small bones) that form the spinal canal. The spinal canal is a tunnel that houses your spinal cord and nerves, protecting them from injury. Most vertebrae move to allow for a range of motion. The lowest vertebrae (sacrum and coccyx) are fused together and don’t move.
- Facet joints: These spinal joints have cartilage (a slippery connective tissue) that allows vertebrae to slide against each other. Facet joints let you twist and turn, and they provide flexibility and stability.
- Intervertebral disks: These flat, round cushions sit between the vertebrae and act as your spine’s shock absorbers. Each disk has a soft, gel-like center (nucleus pulposus) surrounded by a flexible outer ring (annulus fibrosus). Intervertebral disks are under constant pressure, which may cause the nucleus pulposus to squeeze out and contact nerves, leading to symptoms like sciatica.
- Spinal cord and nerves: Your spinal cord is a column of nerves that travels through your spinal canal. The cord extends from your skull to your lower back. Thirty-one pairs of nerves branch out through vertebral openings (neural foramen). These nerves carry messages between your brain and muscles.
- Soft tissues: Ligaments connect the vertebrae to hold your spine in position. Muscles support your spine and help you move. Tendons connect muscles to bone and help prevent muscle injury while aiding in movement.
What are the segments of the spine?
Thirty-three vertebrae make up five distinct spine segments. Starting at your neck and going down toward your tailbone, the segments of your spine include:
- Cervical spine (neck): The top part of your spine has seven vertebrae (C1 to C7). These neck vertebrae allow you to turn, tilt and nod your head. The cervical spine makes an inward C-shape called a lordotic curve.
- Thoracic spine (middle back): The thoracic part of your spine has 12 vertebrae (T1 to T12). Your ribs attach to the thoracic spine. This section of your spine bends out slightly to make a backward C-shape called a kyphotic curve.
- Lumbar spine (lower back): Five vertebrae (L1 to L5) make up the lower part of your spine. Your lumbar spine supports the upper parts of your spine. It connects to your pelvis and bears most of your body’s weight, as well as the stress of lifting and carrying items. The lumbar spine bends inward to create a C-shaped lordotic curve.
- Sacrum: This triangle-shaped bone connects to your hips. The five sacral vertebrae (S1 to S5) fuse (weld together) during fetal development, which means they don’t move. The sacrum and hip bones form a ring called the pelvic girdle.
- Coccyx (tailbone): Four fused vertebrae make up this small piece of bone found at the bottom of your spine. Pelvic floor muscles and ligaments attach to the coccyx.
Nguồn: https://buycookiesonline.eu
Danh mục: Info