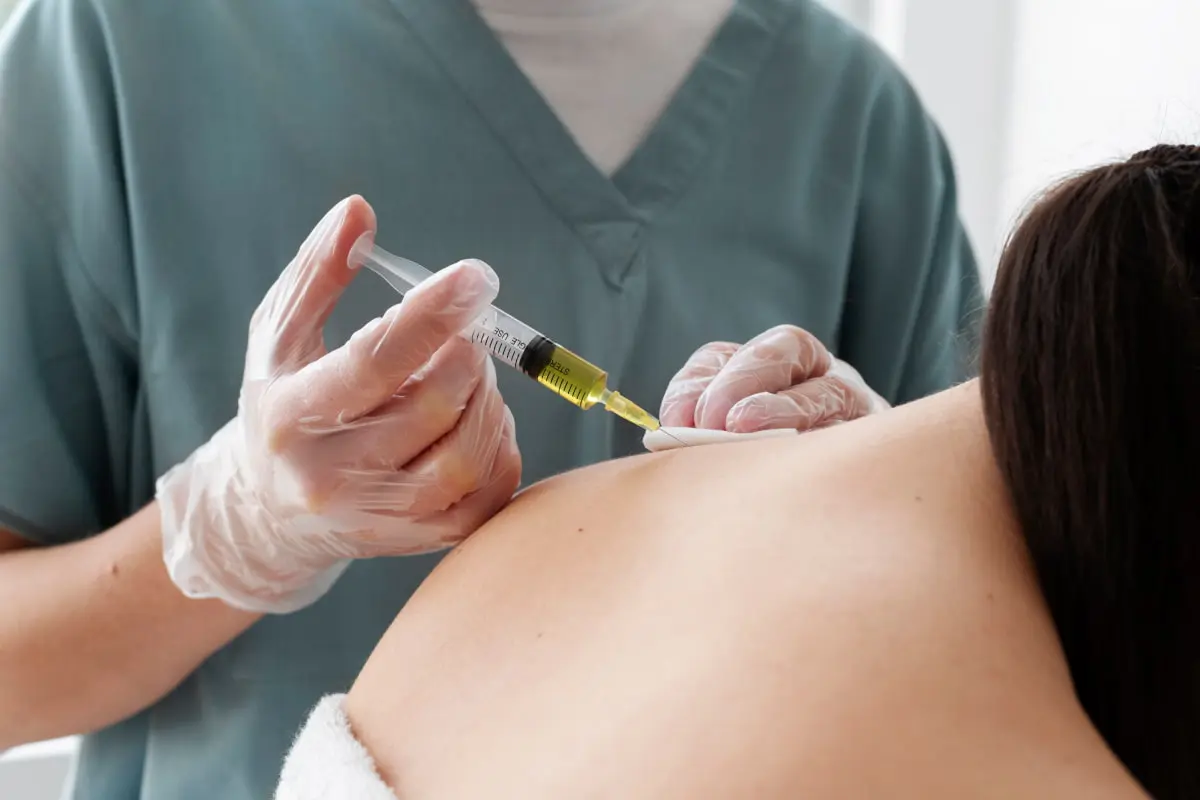
Back pain is now diagnosed even in teenagers. The choice of treatment means is huge:
- from special plasters (tapes);
- to injections into the affected area of the muscle.
But many people with back pain prefer not to go to specialists and engage in self-treatment – they use vibromassage pillows and orthopedic corsets etc.
Bạn đang xem: Botox for Back Pain: Effective Relief for Chronic Discomfort
How safe are such measures? When is it necessary to do a blockade? How to use Botox for back pain? And how does it help with muscle pain? We have answered these and other questions in our article.
Botox for Back Pain: How Does It Work?
Botox has long been famous for its cosmetic applications in reducing facial wrinkles. But, its versatility extends beyond aesthetics. In recent years, Botox has emerged as a potential treatment option for chronic back pain. It offers relief to individuals who have exhausted other avenues of pain management. But how does Botox for muscle pain work?
Back pain often stems from muscle spasms and tension. Various underlying conditions can trigger it. Botox temporarily paralyzes them by blocking the nerve signals that cause muscle contractions. This action helps to ease pain by reducing muscle spasms and relaxing the tense muscles in the back.
The injection process is typically performed under local anesthesia. It is usually guided by imaging techniques for precision. Once injected, Botox takes effect within a few days to a week. It provides relief that can last for several months. The exact duration of pain relief varies from person to person. And it may need periodic checking.
Botox injections for pain is still considered an off-label use. And several studies have shown promising results. It is particularly useful for conditions such as:
- chronic low back pain;
- myofascial pain syndrome;
- muscle spasms caused by conditions like herniated discs or arthritis.
However, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional. He can assess your condition and determine if injections are a treatment option.
As with any medical procedure, potential side effects should be definitely considered. Common side effects include temporary muscle weakness or stiffness near the injection site. In rare cases, more severe complications can occur. It is crucial to receive treatment from a healthcare provider experienced in Botox for back pain.
The Role of Botox in Treating Low Back Pain
Botox plays a significant role in treating low back pain by targeting:
- the underlying muscle spasms;
- tension that contributes to the discomfort.
Xem thêm : Temperature Conversion (Celsius, Fahrenheit)
When injected into the affected muscles, Botox temporarily blocks the nerve signals. They are responsible for muscle contractions, resulting in:
- pain relief;
- relaxation of the muscles.
This approach has shown promise in conditions such as:
- chronic low back pain;
- back pain managemant;
- myofascial back pain.
Botox treatment for low back pain takes no more than 5 minutes. The essence of the procedure is often reduced to the introduction of Botox into the muscle. It helps it relax under the influence of highly toxic protein substances. So the doctor manages to:
- relax spasmed muscles;
- relieve pain and cramps;
- reduce inflammation of a neurogenic nature.
A neurologist conducts botulinum therapy under:
- ultrasound control (if required);
- electrostimulation to consolidate the effect of Botox.
Botox for Muscle Pain: A Potential Solution
Unyielding muscle pain can be an agonizing experience. It limits one’s ability to perform even the simplest of tasks. But fear not, for a potential breakthrough in pain management has emerged. It is Botox injections. Botox has now stepped into the realm of medical marvels. As it offers relief to those burdened by muscle pain.
Muscle pain often arises from spasms and contractions, triggering discomfort. Enter Botox, a veritable wonder drug derived from botulinum toxin. This extraordinary substance works its magic by interrupting the responsible nerve signals. What about the result? A respite from pain and unwinding of those relentlessly tense muscles.
Botox injections for muscle pain provide targeted relief, targeting the root cause of muscle pain. The doctor performs the procedure under careful supervision, ensuring both safety and efficacy. Once injected, Botox takes effect within a matter of days. It delivers profound relief. It can persist for months, allowing individuals to regain control of their lives.
The Effectiveness of Botox Injections for Pain Relief
Botox injections have demonstrated significant effectiveness in providing pain relief for various conditions. The primary mechanism behind Botox’s analgesic effects lies to block nerve signals. By inhibiting muscle activity, Botox can alleviate pain associated with conditions such as:
- chronic migraines;
- cervical dystonia;
- spasticity;
- back pain.
Clinical studies have consistently shown positive outcomes of Botox for muscle pain. So patients experienced reduced pain and improved quality of life. But, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional. So you can determine if Botox injections are suitable for your specific condition. It is good to ensure proper administration for optimal pain relief. The following subsections explore the findings of these studies:
Study 1: Botox for Back Pain Management
The study explores the use of Botox for pain management. They highlight its ability to induce temporary muscle relaxation. Botox inhibits acetylcholine release at motor nerve endings, reducing muscle contraction. It may have direct analgesic effects beyond its neuromuscular actions. Different serotypes and dosages affect the duration of action. Side effects are reversible, and precautions should always be considered for specific conditions. The exact mechanisms of pain relief are not fully understood. But they may involve the suppression of neurotransmitter secretion and reduction of sensitization. Further research is necessary to understand Botox’s:
- efficacy;
- complications;
- analgesic mechanisms in chronic pain disorders.
Study 2: Botox for Chronic Low Back Pain
This prospective study examined the benefits and safety of repeated Botox treatment. Researchers did it for paraspinal muscles in chronic low back pain. Over a 14-month period, 75 patients were assessed using various rating scales for:
- pain intensity, and frequency;
- activities of daily living;
- patient perception of change.
Xem thêm : Cardiology Coding Alert
Of the 39 initial responders (53%), 32 maintained a favorable response. And they repeated treatments for 12 months. The difference in means before and after treatments was statistically significant. Some responders experienced sustained relief for more than 4 months. And a few reported mild flu-like side effects lasting 2-5 days. Overall, the study demonstrated the potential effectiveness. So, you can ensure Botox injections for pain in treating chronic low back pain.
Study 3: Botox for Myofascial Back Pain
A recent study found the efficacy of botulinum toxin type A for treating chronic low back pain. In a single-blind, randomized clinical trial, 50 patients with CLBP received either:
- BoNT-A;
- saline injections in the paraspinal muscles.
Pain levels were measured using:
- a visual analog system (VAS);
- disability.
It was assessed using the Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. After 4 weeks, 76% of patients in the BoNT-A group reported pain relief compared to 20% in the saline group. At 8 weeks, patients in the BoNT-A group experienced:
- greater pain relief;
- functional improvement compared to the saline group.
The study concludes that BoNT-A can effectively improve CLBP with minimal side effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Botox treatment for muscle pain has proven effective for chronic back pain. As it provides targeted muscle relaxation and significant relief. Clinical trials and real-world applications support its ability to reduce:
- muscle spasms;
- tension.
It improves the quality of life for individuals suffering from persistent discomfort. Lone Star Neurology, a specialized medical facility, offers comprehensive services. It includes Botox injections, ensuring personalized care for patients. As neurology advances, Botox holds promise as a valuable tool for back pain management. Seeking guidance from reputable providers like Lone Star Neurology is crucial for treatment. Botox offers a reliable solution for chronic back pain in a minimally invasive manner.
FAQ
- Are Botox injections safe for back pain treatment?
Yes, but the injection of Botox into muscle tissue is performed only on the prescription of a neurologist. The doctor himself determines the treatment scheme and the volume of injection. With him, you can discuss all the features of the procedure and contraindications to it.
- Are there any side effects associated with Botox injections for back pain?
Botox injections for back pain may have temporary side effects. It can localized muscle weakness or stiffness near the injection site. These effects are generally mild and transient, resolving independently within a few weeks.
- How long does the pain relief from Botox injections last?
The duration of pain relief achieved from Botox injections varies among individuals. In most cases, patients can experience significant relief from back pain for several months following the injection. Periodic re-administration of Botox injections may be necessary to maintain optimal pain management outcomes and extend the relief period.
- Can Botox injections completely cure my chronic back pain?
Botox injections can effectively relieve chronic back pain but may not necessarily provide a permanent cure. While Botox can help alleviate muscle spasms and reduce discomfort, it is important to address the underlying causes of your back pain. Botox injections can be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include physical therapy, exercise, lifestyle modifications, and other interventions.
Nguồn: https://buycookiesonline.eu
Danh mục: Info
This post was last modified on November 19, 2024 8:57 am