Medical uses
Terbinafine is the generic antifungal drug Lamisil. It’s the most widely used antifungal medication in use today. Doctors of all types prescribe Lamisil, including the podiatrists and medical doctors at the Beaver Valley Foot Clinic in Cranberry, PA. Lamisil come in Lamisil pill, Lamisil Cream and Terbinifine generic formulations
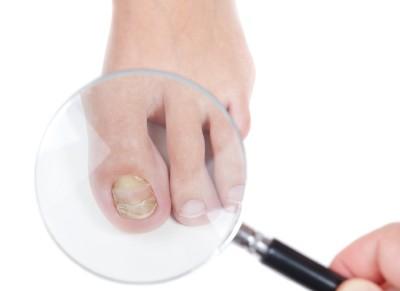
Lamisil belongs to the class of drugs known, unsurprisingly, as antifungals. It’s used to treat many types of fungal infections in almost all regions of the body. In podiatry practices it’s mostly used to combat onychomycosis, e.g. toenail fungus.
Bạn đang xem: Lamisil Antifungal Medication
Using prescription Lamisil tablets
Lamisil is available by prescription only. Your podiatrist or medical doctor will prescribe this drug if you have fungal infections of the toenails (or elsewhere).
As with any prescription medication take Lamisil exactly as prescribed. If you’ve got questions about this antifungal drug talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Lamisil can be taken with or without food, and is usually taken once per day. Both dosage and treatment time are largely determined by the severity of your infection.
By nature, your toenails grow slowly. Even after the fungus has been killed results may not be noticeable. Only after new, healthy nails have grown will the full benefits be achieved. This may take up to several months after you’ve finished your prescription.
Be sure to always finish your prescription. Stopping treatment early may not kill all of the fungal organisms resulting in reinfection. Let your doctor know if your infection persists after treatment or worsens.
Lamisil side effects
Stomach complaints such as abdominal pain and diarrhea can occur while taking Lamisil. These are usually minor. If either of these persists or becomes worse talk to your prescribing doctor.
Not all people who take Lamisil will experience side effects. Also, bear in mind that your doctor has prescribed Lamisil because they believe the benefits outweigh any potential risks.
Rare Side Effects of Lamisil
Although rare, more serious side effects may occur. An altered sense of taste or smell may occur. In the vast majority of cases these symptoms improve after you’ve stopped taking the drug. In very rare cases, however, these changes may become permanent. If you notice any of these sensory change, notify your doctor immediately.
Also contact your doctor immediately if you experience any other more serious side effects. These can include changes in mood such as depression or anxiety. Other extremely rare but potential side effects include changes in vision, unexplained bleeding or bruising, or excessive fatigue. Also look out for kidney problems such as any changes in urine production.
Terbinafine may cause liver disease in very rare cases. If you experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or loss of appetite. Jaundice may also occur. This will appear as a yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes. Contact your doctor immediately if these occur.
Lamisil Allergic Reactions
Serious allergic reactions are also very rare yet possible. Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, a severe rash, and fever. Swelling of the face, tongue, or throat may also occur.
Xem thêm : ‘Hellishly hot’ southern Europe bakes under temperatures topping 104 F
Note that this is not a complete list of all potential side effects. If you experience effects not mentioned above contact your doctor immediately.
To report side effects in the United States, contact the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). They can be reached at (800) FDA-1088 or on the web at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In Canada, report side effects to Health Canada. They can be reached at (866) 234-2345.
Lamisil Precautions
If you’ve allergic to Lamisil or any it’s ingredients tell you doctor or pharmacist. Be sure to consult your pharmacist if there’s any doubt. If you’re allergic to terbinafine there’s a good chance that you may also be allergic to other antifungals. Lamisil, as well as most other drugs in tablet form, contain multiple inactive ingredients. Some are known allergens and can cause severe reactions in sensitive individuals.
Terbinifine is a powerful drug and can be tough on the liver and kidneys. Before taking Lamisil, tell your doctor if you’ve had problems with either of these organs in the past. Also tell your doctor if you have a history of immune disorders, most notably lupus.
While taking Lamisil limit your alcohol intake. Drinking also stresses the liver and can increase your risk of side effects.
Also limit sun exposure while taking Lamisil, as it makes the skin more sensitive to the sun. Avoid both outdoor and indoor tanning. If you do get a sunburn while taking Lamisil, it’s likely to be much worse. When outside, be sure to wear protective clothing and a high SPF (Sun Protection Factor) sunscreen such as SPF 50.
It’s not advisable to take terbinafine while pregnant. You can discuss any potential risks and benefits with your doctor. In most cases treating fungal toenails can wait until after you’ve delivered your baby.
Don’t take terbinafine while breastfeeding. This drug is known to pass into a mother’s milk and can harm your newborn. If you must take Lamisil shortly after the delivery use a high-quality baby formula instead.
Interactions with other drugs
Any drug, including Lamisil, can have adverse effects with other drugs you may be taking. You may need to temporarily discontinue some of your prescriptions while taking terbinafine. Taking another oral antifungal is also an option, although Lamisil is generally regarded as the most effective.
Lamisil may cause other drugs to work differently or not work at all. Additionally, this medication should not be taken with other drugs which stress the liver or kidneys. Drugs with known negative interactions include but are not limited to the following: blood thinners such as Warfarin or Coumadin, and drugs which affect liver enzymes such as Cimetidine and Rifampin. Tricyclic antidepressants should and SSRI antidepressants should also be avoided while taking terbinafine. Beta blockers should also not be combined with Lamisil.
Lamisil Overdose
Accidental overdose is possible with most drugs, including Lamisil. If you suspect an overdose call 911 immediately. It’s also advisable to call your area’s poison control center. The general poison control helpline in the US is (800) 222-1222. In Canada call your provincial poison control center at the same number, (800) 222-1222.
Again, call 911 immediately. Don’t wait to see if the person is going to be “alright.” It is always best to err on the side of caution when drug overdoses or other poisoning is suspected.
Do not share your Lamisil prescription with other people, even if they have the same condition. This drug has been prescribed to you by a qualified physician. They’re aware of you medical history and have determined that the benefits of Lamisil outweigh any possible risks.
Xem thêm : Contact Us
Keep Lamisil and all other medications out of reach of children and pets. Children are smaller than adults so it’s likely that they’ll be affected more so than an adult. This applies to over the counter medications as well.
Missing your dose
If you miss a dose, the final word lies with your doctor or pharmacist. The following guidelines apply to most medications, however.
If it’s close to the time you should have taken your dosage, simply take the missed dose. If it’s close to the time you should take your next dose, skip the missed dose.
Never take a double dose to make up for you missed dose with Lamisil or any other drug unless directed to do so. Lamisil in particular is stressful on the liver and doubling the dose can be harmful.
How long does it typically take for Lamisil to start working?
Lamisil’s effectiveness and the time it takes to start working can vary depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection being treated. For skin infections like athlete’s foot or jock itch, relief of symptoms such as itching and redness may be noticed within a few days of starting treatment. However, it’s crucial to continue using the medication for the prescribed duration, typically around 1 to 2 weeks, to ensure complete eradication of the infection.
For nail fungus, which is notoriously slow to treat due to the slow growth of nails, improvement is gradual. It may take several months of consistent use to see visible changes as the healthy nail grows in. Patience and adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen are key when using Lamisil for nail fungal infections.
Is Lamisil safe for children or elderly patients?
Lamisil can be used in both children and elderly patients, but caution and consultation with a healthcare provider are essential. For children, the safety and efficacy of Lamisil may vary depending on their age and the specific condition being treated. Pediatric dosages and treatment durations should be determined by a healthcare professional. In elderly patients, there may be a higher risk of certain side effects, so monitoring and dosage adjustments might be necessary. Overall, Lamisil can be safe and effective when used appropriately, but individual circumstances and medical history should be considered when determining its suitability for children and elderly individuals.
What should I do if I miss a dose of Lamisil?
If you miss a dose of Lamisil, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s close to the next scheduled dose, skip the missed one. Do not double dose to make up for a missed one. Consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
Storing Lamisil
Store this drug in a cool, dry place which isn’t exposed to direct sunlight. Don’t store in bathrooms or other humid places.
Be sure to pay attention to the expiration date on Lamisil and other drugs. Many medications lose potency with time. Don’t flush expired medications or dispose of them down the drain unless instructed to do so. When in doubt, contact your pharmacist. Also note that many pharmacists have medication disposal programs.
Technical information on Lamisil (turbinafine)
Terbinafine hydrochloride appears as a white crystalline powder. It’s grains are extremely fine. While only slightly soluble in water at standard temperature and pressure, it is readily soluble in ethanol. Other common solvents in which turbinafine is freely soluble include other alcohols such as methanol. It is also freely soluble in methylene chloride.
Per USP (United States Pharmacopeia) each tablet contains 250 mg base terbinafine hydrochloride.
Excipients and binders include the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, sodium starch glycolate, and colloidal silicon.
Nguồn: https://buycookiesonline.eu
Danh mục: Info
This post was last modified on December 14, 2024 10:49 am