Where are bones located?
You have bones throughout your body. They support you from head to toe — literally.
How many bones are in the human body?
Adults have between 206 and 213 bones. Babies are usually born with 270 bones that grow together and fuse into their adult skeleton.
Bạn đang xem: Bones
Xem thêm : School Health Center Improves Care for Students
It might be surprising to learn that some people have more bones than others. The range of bones people can have comes from differences in people’s skeletons, such as:
- Having a different number of ribs.
- Having fewer vertebrae (the bones in your spine).
- If you have fewer digits (fingers or toes) than usual, you’ll have fewer bones.
What do bones look like?
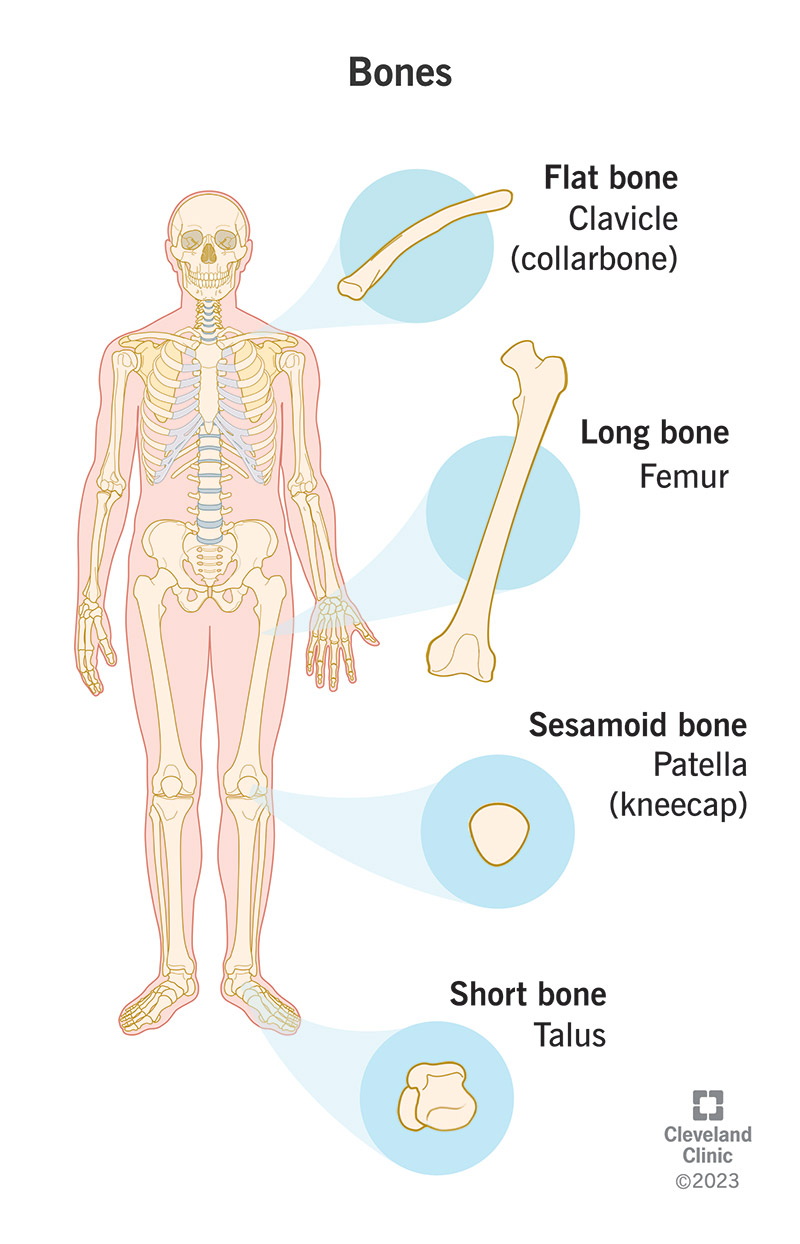
Healthcare providers usually classify bones based on their shape and size, including:
- Long bones: Long bones are exactly what they sound like — the longest bones in your body, especially in your arms and legs. Examples of long bones include the femur (your thigh bone) and the humerus (your upper arm bone). The two bones in your lower leg — the tibia (your shin bone) and fibula (your calf bone) — are also long bones.
- Short bones: Short bones are thinner and weaker than long bones. The bones in your hands and wrists and the talus bone in your ankle are all short bones.
- Flat bones: Flat bones are wider and less round than other bones. The plates that make up your skull, your ribs and the clavicle (your collarbone) are flat bones.
- Sesamoid bones: Sesamoid bones are rooted in tendons or muscles. Other bones are connected to other tissues, but sesamoid bones are embedded directly in them. The patella (your kneecap) and some metacarpal bones in your hands are sesamoid bones.
What are bones made of?
Xem thêm : Wisdom Teeth Extraction Tips and Recovery | Thrive Dental and Orthodontics
Bones are made of cells and proteins. The cortex is the rigid, hard outer layer. It’s the thick shell you see in most illustrations or photos of bones. Cancellous bone (spongy bone) is inside the cortex. It’s much less dense and more flexible. Cancellous bone contains your bone marrow.
Your bones replace their own cells throughout your life. Special cells called osteoblasts and osteoclasts automatically grow and replace your bone tissue. Osteoblasts form new bone tissue. Osteoclasts break down old bone tissue to make room for new, healthier tissue to replace it.
Nguồn: https://buycookiesonline.eu
Danh mục: Info
This post was last modified on December 15, 2024 5:59 am
