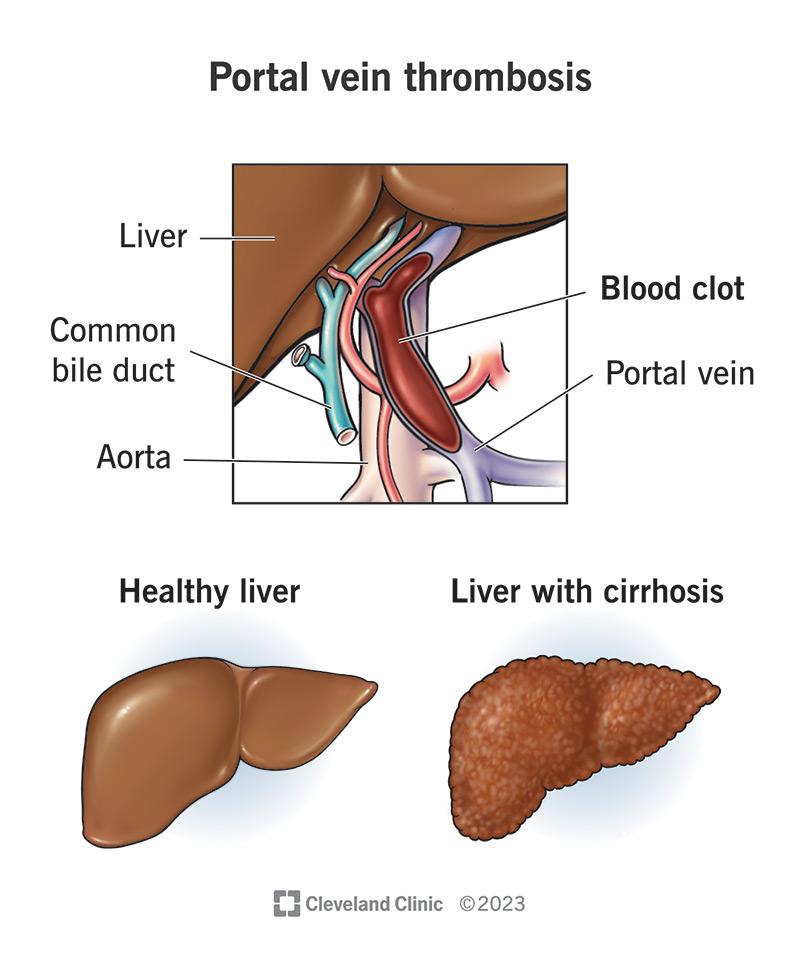
What is portal vein thrombosis?
Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) that narrows or blocks your portal vein. This vein carries blood to your liver from organs in your abdomen (belly). Clots can also develop in your portal vein’s branches (inside your liver) or the blood vessels that drain into your portal vein (superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein).
Portal vein thrombosis is a serious condition, but it often causes no symptoms. So, you may not know you have a blood clot until a healthcare provider finds it through testing or you develop complications, like portal hypertension. Such complications are serious and life-threatening without treatment. Common symptoms include vomiting blood and rectal bleeding (blood in your poop). If you have these symptoms, seek medical care immediately.
Bạn đang xem: Portal Vein Thrombosis
People with cirrhosis face a higher risk of portal vein thrombosis and its complications. Many other medical conditions, like certain blood clotting disorders, can also raise your risk. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider if you have risk factors for portal vein thrombosis. Your provider will make sure you receive appropriate screenings to diagnose and treat issues as early as possible.
Types of portal vein thrombosis
Healthcare providers classify PVT into two main types based on who’s affected:
- Cirrhotic portal vein thrombosis: This is the formation of a portal vein thrombus in people who have cirrhosis (scarring of the liver). This type is more common.
- Non-cirrhotic portal vein thrombosis: This is the formation of a portal vein thrombus in people who don’t have cirrhosis.
This distinction is important in managing the condition. For example, providers often make treatment decisions based on whether or not you have cirrhosis.
Xem thêm : Anatomy and Physiology I
Cirrhosis can also affect your prognosis (outlook) by raising your risk for complications. However, providers continue to learn more about both types of portal vein thrombosis and how to lower your risk for complications. Talk to your provider about your treatment options and what you can expect.
How common is this condition?
Portal venous thrombosis is relatively uncommon in people without liver disease. But the risk is higher among certain groups, including people with cirrhosis. As many as 1 in 4 people with cirrhosis develop PVT. This is because scar tissue in your liver slows down your blood flow, and slow blood flow raises your risk of a blood clot.
What are the complications of portal vein thrombosis?
Complications depend on the exact location of the clot and any underlying conditions you have. Possible complications include:
- Esophageal varices.
- Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding.
- Mesenteric ischemia.
- Portal hypertension.
- Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen).
Nguồn: https://buycookiesonline.eu
Danh mục: Info
This post was last modified on December 5, 2024 7:26 am